Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Tsubata, Yasuhiro; Sato, Takumi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(3), p.97 - 107, 2023/08
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency has chosen nitride fuel as the first candidate for the transmutation of long-lived minor actinides (MA) using accelerator-driven systems (ADS). The pyrochemical method has been considered for reprocessing spent MA nitride fuels, because their decay heat should be very large for aqueous reprocessing. This study was conducted to investigate the effect of decay heat on the pyrochemical reprocessing of MA nitride fuels. On the basis of the estimated decay heats and the temperature limits of the materials that are to be handled in pyrochemical reprocessing, quantities adequate for handling in argon gas atmosphere were evaluated. From these considerations, we proposed that an electrorefiner with a diameter of 26 cm comprising 12 cadmium (Cd) cathodes with a diameter of 4 cm is suitable. On the basis of the size of the electrorefiner, the number necessary to reprocess spent MA fuels from 1 ADS in 200 days was evaluated to be 25. Furthermore, the amount of Cd-actinides (An) alloy to produce An nitrides by the nitridation-distillation combined reaction process was proposed to be about one-quarter that of Cd-An cathode material. The evaluated sizes and required numbers of equipment support the feasibility of pyrochemical reprocessing for MA nitride fuels.
Nishino, Saki; Okada, Jumpei; Watanabe, Kazuki; Furuuchi, Yuta; Yokota, Satoru; Yada, Yuji; Kusaka, Shota; Morokado, Shiori; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-011, 39 Pages, 2023/06
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) which shifted to decommissioning phase in 2014 had nuclear fuel materials such as the spent fuel sheared powder, the diluted plutonium solution and the uranium solution in a part of the reprocessing main equipment because TRP intended to resume reprocessing operations when it suspended the operations in 2007. Therefore, we have planned to remove these nuclear materials in sequence as Flush-out before beginning the decommissioning, and conducted removal of the spent fuel sheared powder as the first stage. The spent fuel sheared powder that had accumulated in the cell of the Main Plant (MP) as a result of the spent fuel shearing process was recovered from the cell floor, the shearing machine and the distributor between April 2016 and April 2017 as part of maintenance. Removing the recovered spent fuel sheared powder was conducted between June 2022 and September 2022. In this work, the recovered powder was dissolved in nitric acid at the dissolver in a small amount in order to remove it safely and early, and the dissolved solution was sent to the highly radioactive waste storage tanks without separating uranium and plutonium. Then, the dissolved solution transfer route was rinsed with nitric acid and water. Although about 15 years had passed since previous process operations, the removing work was successfully completed without any equipment failure because of the organization of a system that combines veterans experienced the operation with young workers, careful equipment inspections, and worker education and training. Removing this powder was conducted after revising the decommissioning project and obtaining approval from the Nuclear Regulation Authority owing to operating a part of process equipment.
Watanabe, Kazuki; Kimura, Norimichi*; Okada, Jumpei; Furuuchi, Yuta; Kuwana, Hideharu*; Otani, Takehisa; Yokota, Satoru; Nakamura, Yoshinobu
JAEA-Technology 2023-010, 29 Pages, 2023/06
The Krypton Recovery Development Facility reached an intended technical target (krypton purity of over 90% and recovery rate of over 90%) by separation and rectification of krypton gas from receiving off-gas produced by the shearing and the dissolution process in the spent fuel reprocessing at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) between 1988 and 2001. In addition, the feasibility of the technology was confirmed through immobilization test with ion-implantation in a small test vessel from 2000 to 2002, using a part of recovered krypton gas. As there were no intentions to use the remaining radioactive krypton gas in the krypton storage cylinders, we planned to release this gas by controlling the release amount from the main stack, and conducted it from February 14 to April 26, 2022. In this work, all the radioactive krypton gas in the cylinders (about 7.1 10
10 GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7
GBq) was released at the rate of 50 GBq/min or less lower than the maximum release rate from the main stuck stipulated in safety regulations (3.7 10
10 GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
GBq/min). Then, the equipment used in the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas and the main process (all systems, including branch pipes connected to the main process) were cleaned with nitrogen gas. Although there were delays due to weather, we were able to complete the controlled release of radioactive krypton gas by the end of April 2022, as originally targeted without any problems such as equipment failure.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Nishida, Naoki; Kobayashi, Daisuke; Nemoto, Ryo*; Hayashi, Hiroyuki*; Kitao, Takahiko; Kuno, Takehiko
JAEA-Technology 2023-004, 30 Pages, 2023/06
Glove-box gloves, that are used for handling nuclear fuel materials at the Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP) of the Japan Atomic Energy Agency, have an expiration date by internal rules. All gloves are replaced at a maximum of every 4-year. However, degrees of glove deterioration varies depending on its usage environment such as frequency, chemicals, and radiation dose. Therefore, physical properties such as tensile strength, elongation, hardness of gloves are measured and technical evaluation method for the glove life-time is established. It was found that gloves without any defects in its appearance have enough physical properties and satisfies the acceptance criteria values of new gloves. Thus, it was considered that the expired gloves could be used for total of 8-year, by adding 4-year of new glove life-time. In addition, the results of extrapolation by plotting the glove's physical properties versus the used years showed that the physical properties at 8-year is on the safer side than the reported physical properties of broken glove. Also, the data are not significantly different from the physical properties of the long-term storage glove (8 and 23 years). Based on these results, life-time of gloves at TRP is set to be 8-year. The frequency of glove inspections are not changed, and if any defects is found, the glove is promptly replaced. Thus, the risk related to glove usage is not increased. The cost of purchasing gloves, labor for glove replacement, and the amount of generated waste can be reduced by approximately 40%, respectively, resulting in more efficient and rationalized glove management.
Fukaya, Yuji; Maruyama, Takahiro; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi; Higuchi, Hideaki
JAEA-Research 2023-002, 19 Pages, 2023/06
A study on disposal of waste derived from commercial High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor ("HTGR") has been performed. Because of significant difference between the reprocessing of Light Water Reactor ("LWR") and that of HTGR due to difference in structures of the fuel, adoptability of the laws relating to reprocessing waste disposal, which is enacted for LWR, to HTGR waste should be confirmed. Then, we compared the technologies and waste of reprocessing and evaluated radioactivity concentration in graphite waste by activation and contamination based on whole core burn-up calculation. As a result, it was found that SiC residue waste should be disposed of into a geological repository as 2nd class designated radioactive waste in the Designated Radioactive Waste Final Disposal Act (Act No.117 of 2000), by way of amendment of the applicable order, same as hull and end-piece of LWR, and graphite waste should be shallowly disposed of than geological disposal as 2nd class waste for pit disposal in the Act on the Regulation of Nuclear Source Material, Nuclear Fuel Material and Reactors (Act No.166 of 1957) same as a channel box of LWR.
Nuclear Science and Engineering Center; Fuel Cycle Design Office; Plutonium Fuel Development Center; Nuclear Plant Innovation Promotion Office; Fast Reactor Cycle System Research and Development Center; J-PARC Center
JAEA-Review 2022-052, 342 Pages, 2023/02
This report summarizes the current status and future plans of research and development (R&D) on partitioning and transmutation technology in Japan Atomic Energy Agency, focusing on the results during the 3rd Medium- to Long-term Plan period (FY 2015-2021). Regarding the partitioning technology, R&D of the solvent extraction method and the extraction chromatography method are described, and regarding the minor actinide containing fuel technology, R&D of the oxide fuel production using the simplified pellet method, the nitride fuel production using the external gelation method, and pyrochemical reprocessing of the nitride fuel were summarized. Regarding transmutation technology, R&D of technology using fast reactors and accelerator drive systems were summarized. Finally, the new facilities necessary for the future R&D were mentioned.
Fukaya, Yuji; Goto, Minoru; Ohashi, Hirofumi
Annals of Nuclear Energy, 181, p.109534_1 - 109534_10, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)Feasibility of reprocessing of High Temperature Gas-cooled Reactor (HTGR) spent fuel by existing Plutonium Uranium Redox EXtraction (PUREX) plant and technology has been investigated. The spent fuel dissolved solution includes approximately 3 times amount of uranium-235 and 1.5 times amount of protonium because of the 3 times higher burnup compared with that of Light Water Reactor (LWR). Then, the heavy metal of the spent fuel is planned to be diluted to 3.1 times by depleted uranium to satisfy the limitation of Rokkasho Reprocessing Plant (RRP) plant. In the present study, recoverability of uranium and plutonium with the dilution is confirmed by a simulation with a reprocessing process calculation code. Moreover, the case without the dilution from the economic perspective is investigated. As a result, the feasibility is confirmed without the dilution, and it is expected that the reprocessed amount is reduced to 1/3 compared with a diluted case even though the facility should be optimized from the perspective of mass flow and criticality.
 (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd and chlorination of MPd using cadmium chloride
using cadmium chlorideHayashi, Hirokazu; Shibata, Hiroki; Sato, Takumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 332(2), p.503 - 510, 2023/02
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)The formation of MPd (M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu
(M = Gd, Np) by the reaction of MN with Pd at 1323 K in Ar gas flow was observed. Cubic AuCu -type GdPd
-type GdPd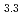 (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) and NpPd
0.0001 nm) and NpPd (
( = 0.4081
= 0.4081  0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi
0.0001 nm) were identified, respectively. The product obtained from the reaction of NpN with Pd contained additional phases including the hexagonal TiNi -type NpPd
-type NpPd . Chlorination of the MPd
. Chlorination of the MPd (M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl
(M = Gd, Np) samples was accomplished by the solid-state reaction using cadmium chloride at 673 K in a dynamic vacuum. Pd-rich solid solution phase saturated with Cd and an intermetallic compound PdCd were obtained as by-products of MCl formation.
formation.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Horigome, Kazushi; Kuno, Takehiko
Applied Radiation and Isotopes, 190, p.110460_1 - 110460_7, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:31.61(Chemistry, Inorganic & Nuclear)Gravimetric measurement of U content in UO with ignition in the air has been investigated. The ignition temperature, ignition time and aliquot sample mass are optimized as 900
with ignition in the air has been investigated. The ignition temperature, ignition time and aliquot sample mass are optimized as 900 C, 60 minutes, and 1 g, respectively. The method is validated by IDMS with uncertainty estimation. The obtained result by gravimetry is 0.78236
C, 60 minutes, and 1 g, respectively. The method is validated by IDMS with uncertainty estimation. The obtained result by gravimetry is 0.78236 0.00051 g/g (k=2) and agreed with IDMS value within its uncertainty. It has been found that U in UO
0.00051 g/g (k=2) and agreed with IDMS value within its uncertainty. It has been found that U in UO can be measured accurately and precisely by gravimetry.
can be measured accurately and precisely by gravimetry.
Omori, Kazuki; Yamauchi, Sho; Yanagibashi, Futoshi; Sasaki, Shunichi; Wada, Takuya; Suzuki, Hisanori; Domura, Kazuyuki; Takeuchi, Kenji
Nihon Hozen Gakkai Dai-18-Kai Gakujutsu Koenkai Yoshishu, p.245 - 248, 2022/07
Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), which is shifted to decommissioning stage, stores large amount of high-level radioactive liquid waste (HLLW). Although TRP is implementing vitrification of HLLW to reduce the risks related to HLLW storage, additional 20 years are required to complete vitrification of HLLW. Therefore, TRP is implementing safety countermeasure related to seismic resistance of HLLW storage facility as one of the top priorities. The results of the seismic evaluation indicate that although the facility itself is seismically resistant, there is a risk of insufficient binding force acting between the facility and the surrounding ground. Thus, replacement of the surrounding ground with concrete is performed. Since the countermeasures, to protect existing buries structure and coordinate with the other construction projects around the site, are required, the dedicated team was setup to handle the process and safety management of the concrete replacement construction.
Tashiro, Shinsuke; Uchiyama, Gunzo; Ono, Takuya; Amano, Yuki; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Abe, Hitoshi
Nuclear Technology, 208(7), p.1205 - 1213, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Nuclear Science & Technology)A clogging behavior of a high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filter at solvent fire accidents for reprocessing facilities has been studied. In this study, the burning rates of 30% tri-butyl phosphate (TBP)/dodecane (DD) mixed solvent and DD solvent and the differential pressure ( P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the
P) of a high airflow typed HEPA filter applied in the actual facilities in Japan were measured. It was confirmed that the mainly burned was DD at the early stage of the mixed solvent burning and the TBP at the late stage. Furthermore, it was found that the  P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P
P rapidly rose at the late stage of the mixed solvent burning. The increase of the release ratio of the unburned particulate composition (TBP, its degraded solvent and inorganic phosphorus (P O
O )) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the
)) was considered to contribute to the rapid rise. The correlating formulas with the  P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of
P and the mass of the loading particulates, except for the region of the rapid rise of  P, could be induced.
P, could be induced.
Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Materials Transactions, 63(4), p.538 - 544, 2022/04
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The time dependence of the corrosion behavior of tantalum (Ta), which is used in nuclear fuel reprocessing equipment, in sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solutions was investigated by immersion tests, and the mechanism of the time dependence was examined via surface observations and electrochemical measurements. The immersion tests were conducted at room temperature with NaOH concentrations ranging from 1 to 7 mol/L for immersion periods of 24 to 168 h. The corrosion rate increased with the NaOH concentration but peaked with the immersion period and then decreased. The time to peak of the corrosion rate was shorter with higher NaOH concentration. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and Raman spectra of the surfaces of the specimens immersed in the 7 mol/L NaOH solution for more than 48 h showed Na Ta
Ta O
O formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na
formation. The polarization resistance decreased with immersion time for all NaOH concentrations up to about 24 h after immersion. Thereafter, the polarization resistance increased with immersion time in 7 mol/L NaOH solution and remained almost constant in the other NaOH concentrations. Findings suggested that the change in the corrosion rate was affected by the film formation during immersion, since the time dependence of the polarization resistance and the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance had the same tendencies. The precipitation film was mainly Na Ta
Ta O
O formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
formed by the dissolution of the passivity film on Ta.
Fujii, Yutaka*; Takada, Chie
FBNews, (540), p.7 - 11, 2021/12
no abstracts in English
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Suzuki, Masafumi*
Gijutsushi, (659), p.4 - 7, 2021/11
The regulatory standards for nuclear facilities were revised, reflecting the lessons learned from Fukushima-Daiichi NPS accident. Many requirements for safety measures, in case there are natural disaster or severe accidents, are added for nuclear fuel cycle facilities. Aiming achievement of the nuclear fuel cycle, various safety measures for conforming to new regulatory standard and improving, have been taken at Rokkasho reprocessing plant.
 I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C records in a modern coral from Rowley Shoals off northwestern Australia reflect the 20th-century human nuclear activities and ocean/atmosphere circulations
C records in a modern coral from Rowley Shoals off northwestern Australia reflect the 20th-century human nuclear activities and ocean/atmosphere circulationsMitsuguchi, Takehiro; Okabe, Nobuaki*; Yokoyama, Yusuke*; Yoneda, Minoru*; Shibata, Yasuyuki*; Fujita, Natsuko; Watanabe, Takahiro; Kokubu, Yoko
Journal of Environmental Radioactivity, 235-236, p.106593_1 - 106593_10, 2021/09
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:35.21(Environmental Sciences)For a contribution to developing the usage of iodine-129 ( I) as a tracer of deep-seated fluid,
I) as a tracer of deep-seated fluid,  I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C were measured for annual bands (AD 1931-1991) of a modern coral collected from Northwestern Australia; the measurements were performed using the JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV for
C were measured for annual bands (AD 1931-1991) of a modern coral collected from Northwestern Australia; the measurements were performed using the JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV for  I/
I/ I and an AMS facility of the University of Tokyo for
I and an AMS facility of the University of Tokyo for 
 C. Results indicate that both
C. Results indicate that both  I/
I/ I and
I and 
 C distinctly increase from 1950s. The
C distinctly increase from 1950s. The 
 C increase can be ascribed to atmospheric nuclear tests, while the
C increase can be ascribed to atmospheric nuclear tests, while the  I/
I/ I increase is due to nuclear-fuel reprocessing as well as atmospheric nuclear tests. These results are in good agreement with previous studies, indicating that the
I increase is due to nuclear-fuel reprocessing as well as atmospheric nuclear tests. These results are in good agreement with previous studies, indicating that the  I/
I/ I measurement by JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV has been further developed.
I measurement by JAEA-AMS-TONO-5MV has been further developed.
Yoshinaka, Kazuyuki; Shimizu, Kazuyuki; Sugiyama, Takayuki
JAEA-Review 2021-008, 112 Pages, 2021/07
We had drastically been improving quality assurance system for Tokai Reprocessing Plant (TRP), through applying new regulatory requirements, giving up ISO certification from FY2012 to 2019. In revising QA system, it is obviously necessary to satisfy the regulatory requirements, but it is important to continuously improve the QA system considering effectiveness to safety performance based on earlier experiences. In this report, the background of QA system revision, interpretation and thinking way of conformation and application to new regulation and "Application Guide to Quality Assurance Code for Safety in Nuclear Power Plants (JEAC 4111)" to TRP, issues considered. And matters that require attention for future QA activities are described. Key points are "in work processes planning, relationship with other sections and responsibility boundaries should be clearly defined with such as flow chart", "to manage decision-making processes is important, including input information, judgment criteria and so on", "concerning process monitoring and measurement, not only focusing on scheduling but also viewpoints toward conditions of facilities/systems, conformance to regulatory requirements and process improvement are necessary", and "in documentation, matching for existing system, clear relation to other fundamental documents are necessary".
Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Zairyo To Kankyo, 70(6), p.192 - 198, 2021/06
The time dependence of corrosion behavior on tantalum used in nuclear fuel reprocessing equipment in sodium hydroxide solution was investigated by immersion corrosion tests, and the mechanism of aging change was discussed from surface observations and electrochemical measurements. The immersion tests were carried out at room temperature with NaOH concentrations ranging from 1 to 7 mol/L and immersion times ranging from 24 to 168 hr, respectively. The corrosion rate increased with NaOH concentration, but peaked with immersion time and then decreased. The time to peak of corrosion rate was shorter with higher NaOH concentration. The SEM observations and Raman analysis at the surface of the specimens that were cleaned and weighed after the immersion test did not show any film formation. On the other hand, the polarization resistance showed a constant value or an increase after a decrease immediately after immersion. It is suggested that the change in corrosion rate is affected by the formation of film by immersion, since the value of polarization resistance is almost the same as the sum of film resistance and charge transfer resistance. The film was considered to be mainly Na Ta
Ta O
O formed by the dissolution of Ta.
formed by the dissolution of Ta.
Yamamoto, Masahiko; Do, V. K.; Taguchi, Shigeo; Kuno, Takehiko; Takamura, Yuzuru*
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 327(1), p.433 - 444, 2021/01
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Chemistry, Analytical)A simple, practical, and reliable analytical method for determination of Na, K, Ca, Sr, and Ba by liquid electrode plasma optical emission spectrometry is developed. Appropriate emission lines for quantification, interferences from co-existing elements, and effect of measurement conditions with cell damage have been investigated. The spike and recovery tests using actual sample have been performed for method validation, and negligible sample matrix effect has been observed. Consequently, the method is successfully applied to several radioactive wastes. The obtained data have been agreed well with data from computer calculation and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry within 10% difference.
Yoshida, Naoki; Ono, Takuya; Yoshida, Ryoichiro; Amano, Yuki; Abe, Hitoshi
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(11), p.1256 - 1264, 2020/11
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:71.58(Nuclear Science & Technology)Emphasis has been placed on the behavior of ruthenium (Ru) in the evaporation to dryness accident due to the loss of cooling functions (EDLCF) of high-level liquid waste in fuel reprocessing plants. It is because Ru would form volatile compounds such as ruthenium tetroxide (RuO ) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric acid (HNO
) and could be released into the environment with other coexisting gasses such as nitric acid (HNO ), water (H
), water (H O). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO
O). To contribute to the safety evaluation of this accident, we experimentally evaluated the decomposition and chemical change behavior of the gaseous RuO (RuO
(RuO (g)) under the various atmospheric conditions: temperature and composition of coexisting gasses. As a result, the behavior of the RuO
(g)) under the various atmospheric conditions: temperature and composition of coexisting gasses. As a result, the behavior of the RuO (g) was diverse depending on the atmospheric conditions. In the experiments with the dry air or H
(g) was diverse depending on the atmospheric conditions. In the experiments with the dry air or H O vapor, decomposition of RuO
O vapor, decomposition of RuO (g) was observed. In the experiment with the mixed gas which containing HNO
(g) was observed. In the experiment with the mixed gas which containing HNO , almost no decomposition of the RuO
, almost no decomposition of the RuO (g) was observed, and chemical form of the RuO
(g) was observed, and chemical form of the RuO (g) was retained.
(g) was retained.
Hashikura, Yasuaki*; Ishijima, Yasuhiro; Nakahara, Masaumi; Sano, Yuichi; Ueno, Fumiyoshi; Abe, Hitoshi
Hozengaku, 19(3), p.95 - 102, 2020/10
A plutonium concentrator was selected, and constant load tensile tests with controlled applied potentials and electrochemical tests were conducted in nitric acid and sodium nitrate solutions. From the results, a map which shows the effect of nitric acid concentration to crack initiation potential was drawn. And, it was pointed out that not only the nitric acid but also the nitrate ion coordinated to the nitrate must be considered in evaluating the possibility of stress corrosion cracking.